Facts About Estrogen
Estrogens are a group of hormones produced primarily by the ovaries in women. They can also be produced by the adrenal gland and fat tissue in smaller quantities. It is considered a female hormone, but the testes in men also produce it in very small quantities and contribute to the development of male reproductive organs. It is referred to as a sex hormone as it mainly targets and is produced by the reproductive organs.
Types of Estrogen:
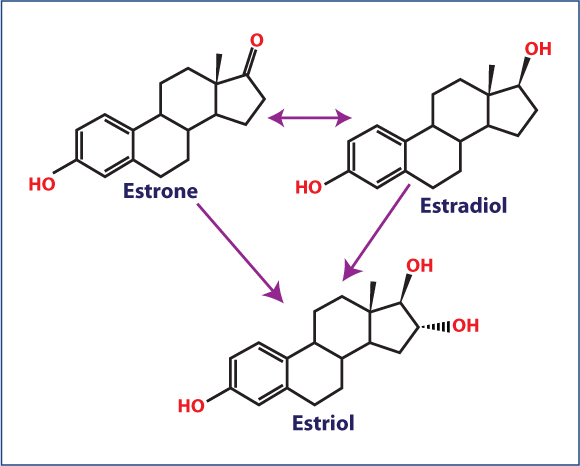
- Estrone (E1): It is only estrogen produced in the body post menopause (when menstruation stops). Fat and muscle tissues may contain small amounts of estrone. The body has the ability to convert estrone to estradiol and estradiol to estrone as required.
- Estradiol (E2): It is a steroid hormone produced by the ovaries. It is the strongest type of estrogen and is most common in women of childbearing age. Imbalance in estradiol can contribute to a range of gynecologic problems such as endometriosis, fibroids and endometrial cancers.
- Estriol (E3): It is a waste product made after the body uses estradiol. It is the weakest form of estrogen. A significant amount of estriol is produced by the placenta during pregnancy. It cannot be converted back to estradiol or estrone.
Functions of Estrogen:
- Reproductive functions
- Development of female secondary sexual characteristics during puberty
- Result in ovulation during the menstrual cycle each month
- Brain: Maintains body temperature and part of the brain responsible for sexual development. It also enhances the effects of feel good chemicals such as serotonin.
- Bone: Preserves bone strength and prevents bone loss. As a result, post-menopausal women are at a risk of developing osteoporosis.
- Liver: Controls metabolic processes such as cholesterol production to protect the heart.
- Skin: Anti-aging properties as it improves collagen content. It also improves thickness, hydration and elasticity of the skin.
Imbalance in Estrogen
Low estrogen levels in women are most commonly due to menopause, removal of ovaries and/or uterus. This results in a variety of symptoms such as:
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Dizziness
- Mood swings
- Sleep disorders
- Anxiety
- Painful intercourse
- Decreased sexual desire
- Dryness and thinning of the vagina
Low estrogen in men can result in:
- Excess belly fat
- Low sexual desire
High estrogen levels in women can result in the following symptoms:
- Weight gain mainly in waist, hips and thighs
- Worsening of premenstrual syndrome
- Fibroids in the uterus
- Fatigue
- Loss of sex drive
- Feeling depressed or anxious
High estrogen levels in men can result in:
- Enlarged breasts (gynecomastia)
- Poor erections
- Infertility
Imbalance in estrogen can have a big impact on health and overall well-being.
Treatment:
Estrogen replacement therapy is used to increase estrogen levels in women and treat the symptoms of menopause. It can also treat delayed puberty, symptomatic vaginal atrophy and breast atrophy. It can help in the prevention of osteoporosis and colon cancer. It has shown to improve skin elasticity, thickness and collagen content, and is used off-label as an anti-aging medication. Estrogen replacement can be done with two types of hormone replacement:
- Traditional hormone replacement: Hormones are derived from the urine of pregnant horses and are chemically similar to the hormones found in the human body. These are the major components of all commercially available hormone replacement products.
- Bioidentical hormone replacement: Hormones are derived from plant based products and are chemically identical to the hormones present in human body. These are not currently FDA approved yet and need to be compounded specially in a compounding pharmacy.
Both types of replacement are equally effective and can be administered in a variety of formulations to meet patient needs. Some common options are:
- Pills
- Creams
- Gels
- Injections
- Patches
- Pellets
Side effects of estrogen replacement include:
- Development of blood clots (DVT and PE)
- Stroke
- Heart disease
- Breast cancer
- Uterine cancer (Can be prevented by using estrogen in combination with progesterone in women who still have their uterus)
Estrogen replacement is a good option for patients who have symptoms associated with low and/or unbalanced estrogen levels. However, it is associated with severe side effects; so it is recommended to use estrogen replacement at the lowest dose for the shortest duration possible.
References:
- Simpson ER, Misso M, Hewitt KN, et al. Estrogen—the good, the bad, and the unexpected. Endocr Rev. 2005;26:322–330.
- What is Estrogen: https://www.hormone.org/hormones-and-health/hormones/estrogen Retrieved on March 4, 2019
- Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy: https://www.healthline.com/health/bioidentical-hormone-replacement-therapy. Retrieved in March 4, 2019
- What are bioidentical hormones: https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/what-are-bioidentical-hormones. Retrieved on March 4, 2019
- Figure 1: Different forms of Estrogen https://restorativemedicine.org/journal/estriol-good-estrogen-advances-updates-clinical-uses/ Retrieved on March 4, 2019



Comments