Intravaginal Boric Acid - An Overview
Intravaginal Boric Acid - An Overview
Boric acid is a weak local anti-infective that is often used topically to for its anti-septic and anti-fungal effects. It is used topically for conditions involving irritated skin, such as chapped or chafed skin.
What does it do?
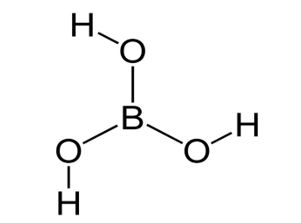
Figure 1: Structure of Boric Acid
Boric acid has both fungistatic and weak bacteriostatic properties which allows it to be used locally for fungal and bacterial vaginal infections in the form of a suppository. The mechanism of action is unknown, but it is thought that the acidic portion of the compound can penetrate the cell wall of fungal organisms and disrupt the cell membrane function. This differs from other antifungal medications that target ergosterol synthesis, which allows boric acid to be used in situations of "azole" drug resistance.
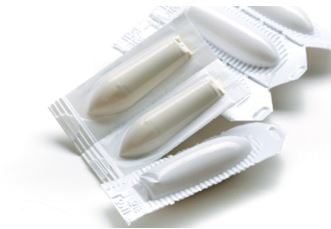
Figure 2: Boric Acid Vaginal Suppositories
How is it made and how is it used?
Boric acid is most often compounded as 600mg vaginal suppositories that are prescribed for use in both bacterial vaginosis and vulvovaginal candidiasis (yeast infection). According to the CDC bacterial vaginosis guidelines, boric acid 600 mg vaginal suppositories (once daily for 21 days) can be used with metronidazole 500mg (twice daily for 7 days), resulting in remission of chronic recurrent bacterial vaginosis.
In addition, the CDC vulvovaginal candidiasis guidelines recommend boric acid 600mg vaginal suppositories (once daily for 14 days) as first line therapy for non-albicans Candida species due to its good coverage. It is not recommended to use boric acid as first line coverage for C. albicans since there are more effective and safe options with shorter regimens as well. However, boric acid can be used in azole-resistant refractory chronic vulvovaginal candidiasis due to its different mechanism of action.
Spectrum of Activity of Boric Acid
| Bacterial | Bacterial Fungal: Good Coverage | Fungal: Possible Coverage |
| Staphylococcus | C. albicans | C. parapsilosis |
| Streptococcus | C. glabrata | C. krusei |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | C. tropicalis | |
| Trichosporon beigelii |
Is it safe?
Systemic toxicity caused by acute poisoning of boric acid can be fatal and affects several organ systems including the central nervous system, kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and skin. The most common side effects associated with this toxicity include abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. Luckily, the risk of systemic toxicity with intravaginal use is extremely small. Boric acid suppositories are generally well-tolerated (with short-term use, long-term is unknown), with the most common side effects seen being burning, redness, and watery discharge. However, boric acid should not be used in pregnant women due to possible teratogenic effects (resulting in birth defects) and an increased risk of miscarriage. There are no known drug-drug interactions related to boric acid use.
Where can you get it?
Boric Acid suppositories can be purchased over the counter as a homeopathic remedy that can be used to "support pH balance" and "support vaginal health." That being said, the long-term effects of boric acid use are unknown, so it is safest to use boric acid suppositories as a short-term treatment pursuant to a prescription for an infection. In that case, 600mg boric acid suppositories can be compounded at a compounding pharmacy and shipped to the patient.
References:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2015). Bacterial Vaginosis. Retrieved from: https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/bv.htm
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2015). Vulvovaginal Candidiasis. Retrieved from: https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/candidiasis.htm
- Nyirjesy P, Seeney SM, Grody MT, et al.: Chronic fungal vaginitis: the value of cultures. Am J Obstet Gynecol 173:820-823, 1995.
- Prutting, SM and Serveny JD: Boric Acid Vaginal Suppositories: A Brief Review. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 6:191-194, 1998.
- Seigel E, Wason S: Boric acid toxicity. Ped Clin North Am 33:363-367, 1986.
- Shinohara YT, Tasker SA: Successful use of boric acid to control azole-refractory Candida vaginitis in a woman with AIDS. J Acquir Immun Defic Syndromes Hum Retrovirology 16:219-220, 1997.
- Swate TE, Weed JC: Boric acid treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Obstet Gynecol 43:893-895, 1974.
- https://www.nutrablast.com/products/nutrablast-boric-acid-suppositories-boric-life-vaginal-intimate-support-600mg?variant=22159147139120
- (Figure 1) Image from: https://www.wikiwand.com/en/Boric_acid
- (Figure 2) Image from: https://www.hysterectomy.org/2016/04/22/vaginal-suppositories-offer-another-treatment-for-vaginal-issues-besides-estrogen-cream/



Comments